The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has developed a complex structure for calculating depreciation. It’s important to understand how each step works so that you can easily find the information needed when depreciating your assets.
The Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) is the depreciation system used for tax purposes in the United States. It allows the capitalized cost of an asset to be recovered in a specified period through annual deductions. Fixed assets are categorized into different classes, each of which has its own depreciation period.
Aside from the MACRS, there are tax incentives that you can apply for, such as Section 179 and bonus depreciation, to accelerate the depreciation of your assets. Section 179 and bonus depreciation allow you to write off significant amounts from the costs of assets in the year the properties are placed in service while MACRS provides depreciation over longer periods of time. This enables businesses to deduct bigger amounts in the earlier years of an asset’s useful life before the depreciation amount decreases in later years.


What are the MACRS systems?
There are two MACRS depreciation systems that can be used for calculating depreciation: the General Depreciation System (GDS) and the Alternative Depreciation System (ADS). Understanding how both systems work will help you identify the depreciation method and recovery period to apply to the assets you need to depreciate.AssetAccountant – saving you from spreadsheets since 2019
1. General Depreciation System (GDS)
The General Depreciation System (GDS) is the most common MACRS system to use, and it uses the 150% or 200% declining balance method in calculating depreciation. The IRS published property classifications under the GDS based on the useful life of the asset so that you can identify the computation for a given type of asset, since each classification has a different recovery period. The table below illustrates how different types of assets are classified based on their useful life. A three-year property classification will include tractors and racehorses over two years old while a five-year property classification will include automobiles, office machinery and computer equipment.


2. Alternative Depreciation System (ADS)
The Alternative Depreciation System (ADS) uses the straight-line depreciation method, providing a longer recovery period for assets that more accurately reflect their income streams than declining balance depreciation. It’s important to note that while the depreciation can be extended using the ADS, the annual depreciation also decreases over time.
If you choose to utilize the ADS for an asset, it is imperative that the system is implemented across all properties within the same asset class that are put into service within the same year.
According to the IRS, a taxpayer is required by law to use the ADS for the following properties:
- Nonresidential real property, residential real property, and qualified improvement property held by an electing real property trade or business.
- Any property with a recovery period of 10 years or more under GDS held by an electing farming business.
- Any tax-exempt use property.
- Any tax-exempt bond-financed property.
- All property used predominantly in a farming business and placed in service in any tax year during which an election not to apply the uniform capitalization rules to certain farming costs is in effect.
- Any property imported from a foreign country for which an Executive Order is in effect because the country maintains trade restrictions or engages in other discriminatory acts.
- Any tangible property used predominantly outside the United States during the tax year.
- Any listed property used 50% or less in a qualified business use during the tax year.
What are the MACRS conventions?
The conventions used in MACRS determine the recovery period of your assets and the depreciation amount you can claim in the year a property is placed in service and in the year a property is disposed of.
The MACRS conventions include:
- Mid-month convention – This applies to real property (i.e. land and all items affixed on the land) which are placed in service and disposed of during a month, providing a one-half month depreciation for the month the property is placed in service or disposed of.
- Mid-quarter convention – If more than 40% of depreciable personal property (i.e. excluding real property) is placed in service during the last quarter of the tax year then use the mid-quarter convention. For a 12-month tax year, 1.5 months of depreciation is allowed for the quarter a property is placed in service or disposed of.
- Half-year convention – If neither the mid-month nor mid-quarter convention applies, a taxpayer will use a half-year convention where an asset placed in service or disposed of during the mid-point of the year. For a 12-month tax year, one-half a year depreciation is allowed for the year the property is placed in service or disposed of.


When to switch from declining balance to straight line depreciation method
Once you’ve identified the MACRS depreciation system, the property classification and MACRS convention to use, you can calculate the depreciation of your asset.
The formula for MACRS depreciation is as follows:

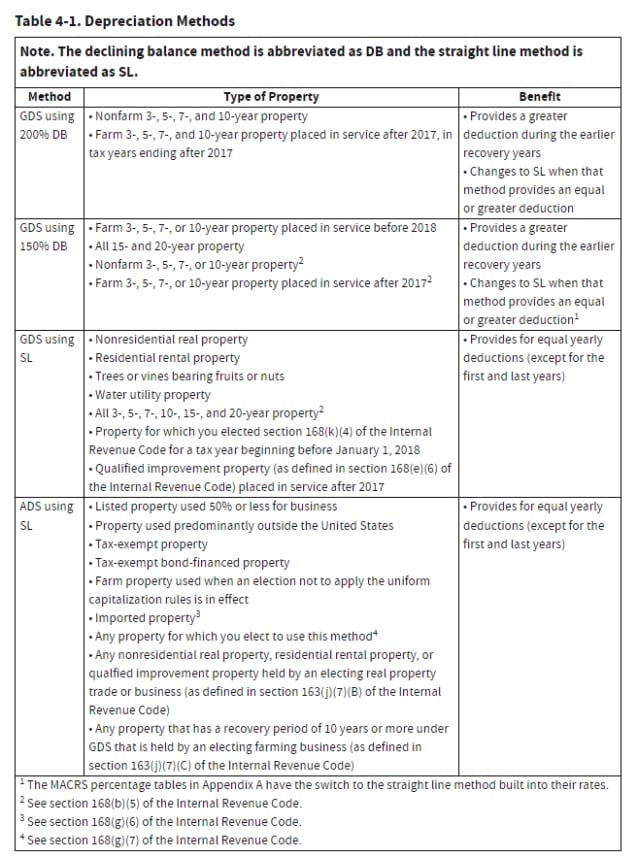
“A” can either be 100%, 150% or 200% depending on the convention used. According to IRS Publication 946, a taxpayer using the general depreciation system is required to use the 150% or 200% declining balance method (depending on their type of property) before changing the depreciation to the straight line method in the first year that the asset provides an equal or greater deduction.
There are key differences between the declining balance method and straight-line method. The declining balance method, or diminishing value, provides a higher deduction in the earlier years of an asset’s life before the amount reduces over time. The straight-line method, or prime cost method, reduces the costs of an asset uniformly over its useful life.
The table below shows the depreciation accounting method used for different types of property. “DB” stands for declining balance while “SL” stands for straight line.
It is possible to manually calculate the MACRS depreciation as long as you have the following information:
- Type of property
- Convention to be used
- Depreciation method to be used
Bear in mind that it can be challenging to develop a spreadsheet that accurately and quickly calculates all of these variables, especially if you have assets with different conventions while switching from declining balance to straight line when needed.
The AssetAccountant™ software can automatically calculate the MACRS depreciation for your assets, as long as you choose the correct classification and convention for your property. This will minimize error-prone calculations and ensure that you complete the IRS Tax Form 4562 with the correct data.
By learning the MACRS systems and conventions as well as the depreciation methods used for different asset classes, you can have a better grasp of how your assets depreciate over time.
If you want to start calculating MACRS depreciation quickly and easily, third-party software can give you accurate information. Sign up for a free trial account with AssetAccountant™.
We take depreciation and leasing seriously
We undertake detailed modelling of fixed asset depreciation and lease calculation rules for both accounting and tax.
We monitor changes to ATO tax rulings and accounting standards like IAS 16 and IFRS 16 so you don’t have to.
And, of course, we are ISO27001 certified.
We take depreciation and leasing seriously
We undertake detailed modelling of fixed asset depreciation and lease calculation rules for both accounting and tax.
We monitor changes to IRS tax rulings and accounting standards like US GAAP and ASC 842 so you don’t have to.
And, of course, we are ISO27001 certified.
We take depreciation and leasing seriously
We undertake detailed modelling of fixed asset depreciation and lease calculation rules for both accounting and tax.
We monitor changes to IRD tax rulings and accounting standards like IFRS 16 so you don’t have to.
And, of course, we are ISO27001 certified.
We take depreciation and leasing seriously
We undertake detailed modelling of fixed asset depreciation and lease calculation rules for both accounting and tax.
We monitor changes to tax rulings and accounting standards like IFRS and US GAAP so you don’t have to.
And, of course, we are ISO27001 certified.
Why our clients love AssetAccountant


Fantastic product - has literally saved me hours of work.


Ever wanted the big company fixed asset system without all the clunkiness and overthinking on the part of the software developers (I'm looking at you Thomson Reuters...)? Well then you need AssetAccountant. It provides just the right mix of complex depreciation calculations and beautiful user interface. It's a system designed by accountants and executed perfectly by developers. The integration is seamless with Xero (you can sign into AA with Xero credentials which is awesome if you are already running Xero on your browser) and journaling synchs are very flexible between the two applications. Then there is the price. I challenge you to find a more robust fixed asset system at these price points. Well done AssetAccountant.
You get me.
I now have my big boy jocks back on for fixed asset management....and they fit!









Ready to kick some assets?
- AssetAccountant is fixed asset software that automates fixed asset depreciation & lease accounting and posts their journals to the General Ledger.
- AssetAccountant combines detailed interpretation of Tax and Accounting rules with a modern user interface design, to simplify the process of creating and maintaining your fixed asset register.
- AssetAccountant is sophisticated enough for Wall Street, user-friendly enough for main street.
- AssetAccountant is for worldwide application 🌎